Crest factor
The crest factor or peak-to-average ratio (PAR) or peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR) is a measurement of a waveform, calculated from the peak amplitude of the waveform divided by the RMS value of the waveform.
It is therefore a dimensionless quantity. While this quotient is most simply expressed by a positive rational number, in commercial products it is also commonly stated as the ratio of two whole numbers, e.g., 2:1. In signal processing applications it is often expressed in decibels (dB).
The minimum possible crest factor is 1, 1:1 or 0 dB.
Contents |
Examples
This table provides values for some normalized waveforms:
| Wave type | Waveform | Peak magnitude (normalized) | RMS value | Crest factor | Crest factor (dB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DC | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.0 dB | |
| Sine wave | 1 | 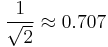 [1] [1] |
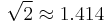 |
3.01 dB | |
| Full-wave rectified sine | 1 | 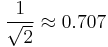 [1] [1] |
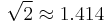 |
3.01 dB | |
| Half-wave rectified sine | 1 | 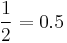 [1] [1] |
 |
6.02 dB | |
| Triangle wave | 1 | 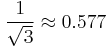 |
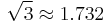 |
4.77 dB | |
| Square wave | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 dB | |
| PWM-Signal | 1 | 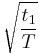 [1] [1] |
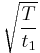 |
|
|
| QPSK | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 dB | |
| 8VSB | 6.5–8.1 dB [2] | ||||
| 64QAM | 1 | 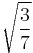 |
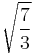 |
3.7 dB | |
 -QAM -QAM |
1 | 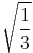 |
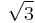 |
4.8 dB | |
| WCDMA downlink carrier | 10.6 dB | ||||
| OFDM | ~12 dB | ||||
| GMSK | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 dB |
Notes: 1. crest factors specified for QPSK, QAM, WCDMA are typical factors needed for reliable communication, not the theoretical crest factors which can be larger.
Digital multimeters
Crest factor is an important parameter to understand when trying to take accurate measurements of low frequency signals. For example, given a certain digital multimeter with an AC accuracy of 0.03 % (always specified for sine waves) with an additional error of 0.2 % for crest factors between 1.414 and 5, then the total error for measuring a triangular wave (crest factor = 1.73) is 0.03 % + 0.2 % = 0.23 %. In acoustics, crest factor is usually expressed in decibels. For example, for a sine wave the 1.414 ratio is 20 log(1.414) or 3 dB. Most ambient noise has a crest factor of around 10 dB while impulsive sounds such as gunshots can have crest factors of over 30 dB. (Note the waveform factor of the half wave sine wave rectified signal should be 2.22 not 1.11)
Peak-to-average ratio (PAR) meter
A peak-to-average ratio meter (Par meter) is a device used to measure the ratio of the peak power level to the time-averaged power level in an electrical circuit. This quantity is known as the peak-to-average ratio (p/a r or PAR). Such meters are used as a quick means to identify degraded telephone channels.
Par meters are very sensitive to envelope delay distortion. They may also be used for idle channel noise, nonlinear distortion, and amplitude-distortion measurements.
The peak-to-average ratio can be determined for many signal parameters, such as voltage, current, power, frequency, and phase.
Applications
- Electrical engineering — for describing the quality of an AC power waveform
- Vibration analysis — for estimating the amount of impact wear in a bearing [3]
- Radio and audio electronics — for estimating the headroom required in a signal chain [4]
- Physiology — for analysing the sound of snoring [9]
References
- ^ a b c d "RMS and Average Values for Typical Waveforms". Archived from the original on 2010-07-21. http://www.webcitation.org/5rPH2bywi.
- ^ http://broadcastengineering.com/mag/broadcasting_transitioning_transmitters_cofdm/
- ^ What Is The “Crest Factor” And Why Is It Used?
- ^ Crest factor analysis for complex signal processing
- ^ Crest factor definition — Rane Pro Audio Reference
- ^ Level Practices in Digital Audio
- ^ Gain Structure — Setting the System Levels, Mackie Mixer Tips
- ^ Setting sound system level controls: The most expensive system set up wrong never performs as well as an inexpensive system set up correctly.
- ^ Palatal snoring identified by acoustic crest factor analysis
This article incorporates public domain material from the General Services Administration document "Federal Standard 1037C" (in support of MIL-STD-188).
External links
- Definition of peak-to-average ratio – ATIS (Alliance for Telecommunications Industry Solutions) Telecom Glossary 2K
- Definition of crest factor – ATIS (Alliance for Telecommunications Industry Solutions) Telecom Glossary 2K
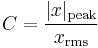
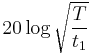 dB
dB